by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
IEEE 802.11 defines how data packets are transmitted over air.
|
Protocol
|
Speed
|
|
802.11a
|
54 Mbits/Sec, 5 GHz
|
|
802.11b
|
11 Mbits/Sec, 2.4 GHz
|
|
802.11g
|
54 Mbits/Sec, 2.4 GHz
|
|
802.11n
|
600 Mbits/Sec 5 or 2.4 GHz
|
WLANs use Access Points to connect nodes to Internet.
WLANs typically use WPA2 (WiFi Procted Access) protocol to secure communication.
by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
LAN (Local Area Network) can use several Network Protocols to define the Network. These protocols are defined at the OSI Data Link Layer
| Protocol |
Cable used |
Topology |
Media Access |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Ethernet |
Twisted Pair or Fiber Optic |
Star |
CSMA/CD |
Fast; Easy setup and maintenance |
Possible Collision issues |
| Token Ring |
Twisted Pair |
Ring |
Token Passing |
Low error rate |
Slow (4 or 16 Mbps) |
| FDDI |
Fiber Optic (Dual counter rotating ring) |
Ring |
Token Passing |
Low error rate. Redundancy. |
Expensive |
| ARCNet |
Coaxial |
Star |
Token Passing |
Predicable Network Performance |
Slow. (Almost extinct) |
Read More
by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
The second layer in OSI model is the Data Link, a very important layer in ensuring Network connectivity and data delivery. Main functions of Data Link Layer are:
- Define Network Protocol (Ex. Ethernet, Token Ring etc)
- Ensure Data is delivered to the correct device across Network
Data Link Layer has two sub layers in them
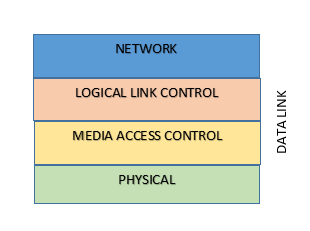
Read More
by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
In OSI Physical layer the following Network Equipment’s are involved.
- Network Interface Card
- Medium (Cables and Connectors)
- Repeaters
- Hubs
Network Interface Cards:
NICs connect a computer to the Network. They can be integrated to the Motherboard or can be a separate Card (PCI,ISA etc).

Read More
by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
In OSI 7 layer model, the Physical layer defines the Networking hardware pertaining to transmitting the electrical (or optical) signals. A major component in this layer is the physical medium that carries the data. This Physical medium is typically a Network cable with appropriate connector.
Digital & Analog Signaling:
Digital: Data is transmitted in pulses (electrical signals on/off)
Analog: Data is transmitted through continues wave with variations in amplitude, frequency and Phase.
Baseband & Broadband Signaling:
Read More
by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
ISO (International Standards Organization) came up with OSI (Open Systems Interconnect) Model ( ISO/IEC 7498-1) in1984 to address the following:
- Inter-operability between systems
- Reduce complexity in understanding Network processes
- Enable Vendors to focus on their layer of interest and not to worry about other layers
There are 7 layers in the OSI model
- Physical
-
Data Link
- Sublayer 1: MAC (Media Access Control)
- Sublayer 2: DLL (Data Link Layer)
- Network
- Transport
- Session
- Presentation
- Application
|
APPLICATION
|
|
PRESENTATION
|
|
SESSION
|
|
TRANSPORT
|
|
NETWORK
|
|
DATA LINK
|
|
PHYSICAL
|
Read More
by Karun Subramanian
on August 9, 2015
A Brute Force attack will take few milliseconds to crack a 4 digit PIN (10,000 possible PINs). Have you ever wondered why the PIN (Personal Identification Number) for most of the commercial ATM cards is only 4 digits ? Some banks do allow you to choose longer PINs but the minimum number of digits is mostly 4.
Despite the smaller length, PIN is still an effective way of securing the ATM card. Here are the reasons why.
Read More

