Virtualization is a technique using which you can run multiple Operating Systems (aka Guest) in a physical server (host) by abstracting (or virtualizing) CPU, Memory, Disk and Network resources. The core component of any virtualization solution is Hypervisor – the software that performs the abstraction of bare metal resources.
Here are the primary benefits of using Virtualization:
- Save cost on hardware
- Centrally manage the infrastructure
- Add effective fault tolerance and high availability
- Dynamically update the infrastructure
The diagram below shows virtualization at a high level.
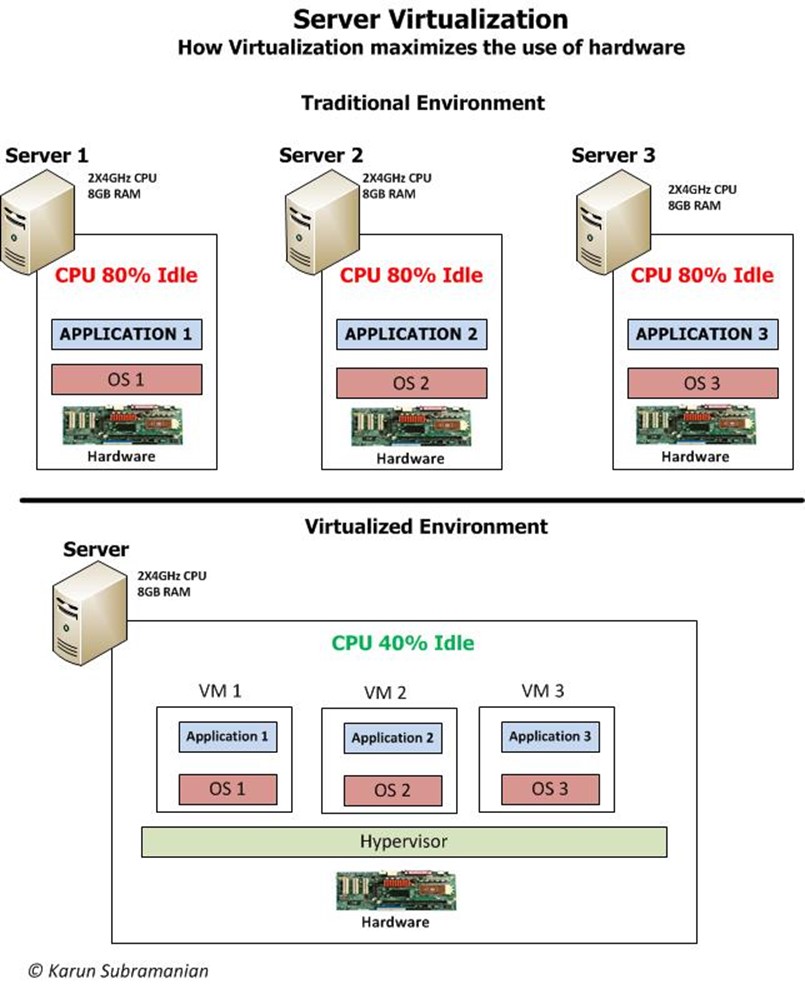
In addition to virtualizing a Server, a pool of servers together can be virtualized as well. In this case, multiple servers (with Hypervisors installed on them) form a virtual datacenter as shown below.
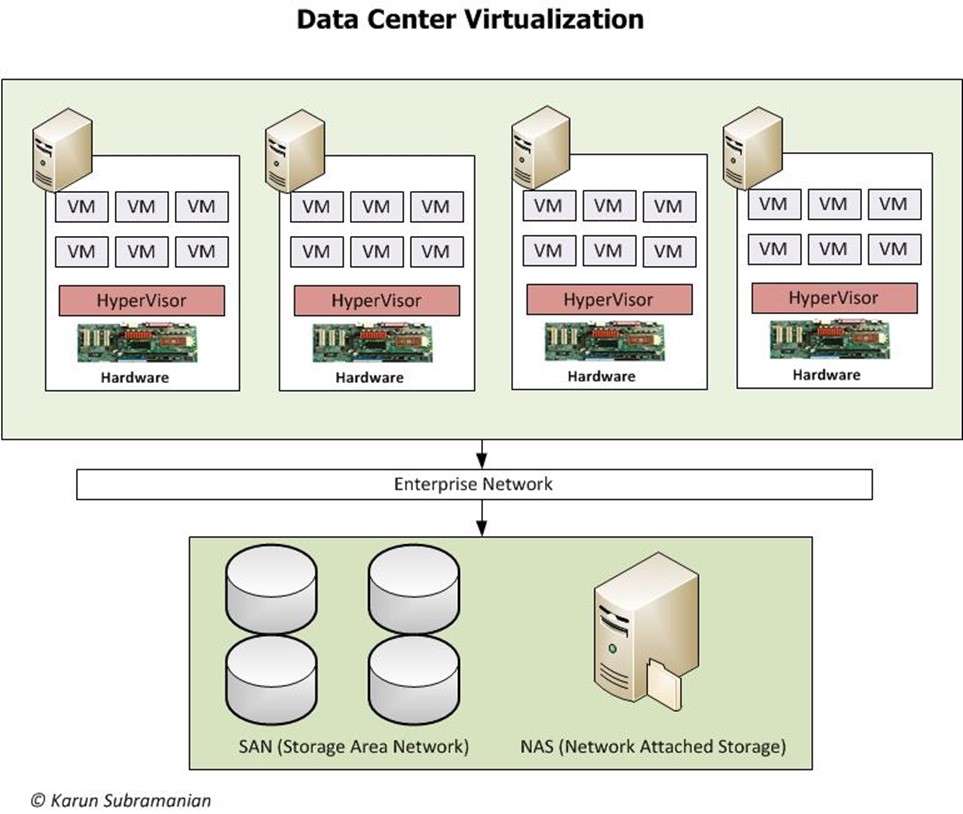
Through centralized management of the virtual environment, virtualization enables a Systems Administrator to view the entire data center as a pool of virtual resources consists of Servers (VMs), Storage and Network. From this pool, he or she can provision computing power to the business as needed.
Application support engineers must be aware of the capabilities of the Virtualized environment to support their applications well. For instance, he or she should know that Disk space can be added to a Virtual machine without taking the VM down. And in most instances CPU and Memory can be added without taking the VM down.
There are three primary vendors in the market today in the virtualization space:
- VMware (EXSi)
- Cirtix (XenServer)
- Microsoft (HyperV)
The following sections provide a high level overview of the capabilities of each of these products.
Comments on this entry are closed.