by Karun Subramanian
on August 29, 2015
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Protocol:
It is a Link-State dynamic routing protocol used primarily in large networks. It routes packets within an AS (Autonomous System) – Interior gateway protocol (IGP). OSPF networks as assigned an Area identifier (32 bit length). The area identifier can be same as the IP address. OSPF can handle duplicate ip addresses without any conflict.
OSPF does not use UDP or TCP but rather directly encapsulated into IP datagrams.
OSPF areas include Backbone area (area 0), Stub area, not so stubby area (NSSA).
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP):
It is a path-vector based dynamic protocol that is widely used in ISP. It is an exterior gateway protocol (EGP)
by Karun Subramanian
on August 27, 2015
There are 5 major WAN technologies available
- Point to Point Link
- Circuit Switched Network
- Packet Switched Network
- High Level Data Link control (HDLC)
- Synchronous Data Link control (SDLC)
Point to Point Link
Uses a public career for establishing WAN connectivity
| Technology |
Details |
| SLIP (Serial Line IP) |
- Enables serial devices such as modems to connect to remote network
- Asynchronous
- Slow speed
- Little or no security
|
| Point to Point Protocol (PPP) |
- Successor of SLIP
- Asynchronous and Synchronous operation
- More security features than SLIP
|
| Point to Point tunneling protocol |
- Relies on PAP,CHAP or EAP to provide encryption
- Developed by Microsoft
- Used in VPNs
|
| Layer 2 Forwarding protocol |
- Used in VPN with PPP
- Little or no security
- Developed by CISCO
|
| Layer 2 Tunneling protocol |
- Used in VPN
- Uses IPSec for encryption
- Uses UDP port 1701
|
Circuit Switched Network
Read More
by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
|
Circuit
|
Speed
|
|
DS0
|
64 Kbits/Sec
|
|
DS1
|
1.544 Mbits/Sec or 2.048 Mbits/Sec
|
|
DS3
|
44.736 Mbits/Sec
|
|
T1
|
1.544 Mbits/Sec
|
|
T3
|
44.736 Mbits/Sec
|
|
E1 (Used in Europe)
|
2.048 Mbits/Sec
|
|
E3 (Used in Europe)
|
34.368 Mbits/Sec
|
|
OC-1 (Synchronous Optical WAN)
|
51.84 Mbits/Sec
|
|
OC-3 (Synchronous Optical WAN)
|
155.52 Mbits/Sec
|
|
OC-12 (Synchronous Optical WAN)
|
622.08 MbitsSec
|
|
OC-48 (Synchronous Optical WAN)
|
2.488 Gbits/Sec
|
|
OC-192 (Synchronous Optical WAN)
|
9.9 Gbits/Sec
|
by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
IEEE 802.11 defines how data packets are transmitted over air.
|
Protocol
|
Speed
|
|
802.11a
|
54 Mbits/Sec, 5 GHz
|
|
802.11b
|
11 Mbits/Sec, 2.4 GHz
|
|
802.11g
|
54 Mbits/Sec, 2.4 GHz
|
|
802.11n
|
600 Mbits/Sec 5 or 2.4 GHz
|
WLANs use Access Points to connect nodes to Internet.
WLANs typically use WPA2 (WiFi Procted Access) protocol to secure communication.
by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
LAN (Local Area Network) can use several Network Protocols to define the Network. These protocols are defined at the OSI Data Link Layer
| Protocol |
Cable used |
Topology |
Media Access |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Ethernet |
Twisted Pair or Fiber Optic |
Star |
CSMA/CD |
Fast; Easy setup and maintenance |
Possible Collision issues |
| Token Ring |
Twisted Pair |
Ring |
Token Passing |
Low error rate |
Slow (4 or 16 Mbps) |
| FDDI |
Fiber Optic (Dual counter rotating ring) |
Ring |
Token Passing |
Low error rate. Redundancy. |
Expensive |
| ARCNet |
Coaxial |
Star |
Token Passing |
Predicable Network Performance |
Slow. (Almost extinct) |
Read More
by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
The second layer in OSI model is the Data Link, a very important layer in ensuring Network connectivity and data delivery. Main functions of Data Link Layer are:
- Define Network Protocol (Ex. Ethernet, Token Ring etc)
- Ensure Data is delivered to the correct device across Network
Data Link Layer has two sub layers in them
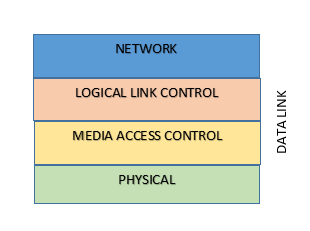
Read More
by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
In OSI Physical layer the following Network Equipment’s are involved.
- Network Interface Card
- Medium (Cables and Connectors)
- Repeaters
- Hubs
Network Interface Cards:
NICs connect a computer to the Network. They can be integrated to the Motherboard or can be a separate Card (PCI,ISA etc).

Read More
by Karun Subramanian
on August 23, 2015
It transports 1 petabit/sec with 100,000 servers talking to each other at 10Gbits/sec. Yes it is sick. This is how Google achieved that feat.
It is no brainer. With the amount of data google indexes (last time I checked, it is all the data from a small network called Internet), there is no way traditional Data Centers and Network Infrastructure can deliver. The underpinning technology that makes companies like Google take giant leap in Network design is SDN aka Software Defined Networking.
Read More

